manual compression test great saphenous vein|varicose veins with gsv : traders Retrograde filling ( trendelenburg test): to assess valvular competency in both communicating veins and saphenous system-Pt supine-Raise one leg to 90o ( to empty venous blood)-Occlude great saphenous vein in the upper thigh by manual compression-Keep the vein occluded ask the pt to stand watch for venous filling in the leg ---- 35 sec 22 de set. de 2022 · LEVAMOS A MC PIPOKINHA PARA DAR UMA VOLTA NA CARONA DO TED. Hardbrazil Produções. 4.6K subscribers. Subscribe. Subscribed. 274. 30K views 1 year ago. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
13 de fev. de 2024 · 3 Vitórias do Al Feiha 2 Empates 0 Vitória do Al Nassr Último jogo: Al Feiha 1 x 3 Al Nassr (Hussein Al-Shuwaish; Anderson Talisca - 2, Otávio), em 28 de .
Manual compression of peripheral vein segments in the standing position with use of pulsed-wave Doppler imaging provides the greatest sensitivity and specificity in discriminating between normal and abnormal vein segments . Biemans A, van den Bos R, Hollestein LM, et al. The effect of single phlebectomies of a large varicose tributary on great saphenous vein reflux. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord 2014;2:179-187. Pittaluga P, Chastanet S. . Reflux was defined as a reversed flow lasting for >0.5 second after manual compression of the calf in the . Continuous variables are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation after the normality test (Kolmogorov-Smirnov . The principle veins of the superficial system are the great saphenous vein (GSV), formerly known as either the greater or long saphenous vein, and the small saphenous vein (SSV), formerly known as the short, .
Retrograde filling ( trendelenburg test): to assess valvular competency in both communicating veins and saphenous system-Pt supine-Raise one leg to 90o ( to empty venous blood)-Occlude great saphenous vein in the upper thigh by manual compression-Keep the vein occluded ask the pt to stand watch for venous filling in the leg ---- 35 seca PA evaluating a pt for valvular competency in the communicating veins of the saphenous system, starts with the pt supine, then elevates one leg to about 90 degree to empty it of venous blood. next, the great saphenous vein in the upper part of the thigh is occluded with manual compression, and the pt stands. the PA keeps the vein occluded .
The great saphenous vein receives branches from the sole via the medial marginal vein at the ankle; in the lower leg, it anastomoses freely with the small saphenous vein, communicates with the anterior and posterior tibial veins via perforator veins (Cockett perforators), and receives many cutaneous veins; near the knee, it communicates with .
manual compression and release of the calf muscles, and SFC reflux by the Valsalva maneuver, both in standing . isons were tested using the 2 test, and the mean compar-isons were tested using the Student t test (paired t test). A . stripping of the great saphenous vein without crossectomy Ecchymosis at D8 101 51.8% Mean surface (cm2) 9.15 The advantage of these methods is that it standardises the compression test and refilling time. . Little flow is observed in a patient with obvious varicose tributaries after manual compression of the vein immediately below the measuring point to improve the outcome, . the great saphenous vein (GSV) pierces the fascia (ostium) to drain into . The Society for Vascular Surgery, the American Venous Forum, and the American Vein and Lymphatic Society recently published Part I of the 2022 clinical practice guidelines on varicose veins. Recommendations were based on the latest scientific evidence researched following an independent systematic review and meta-analysis of five critical issues affecting . Course of the great saphenous vein (GSV) and its related branches, including perforators, are shown at the anteromedial aspect of the right leg. . Filling of the varicose veins can be checked by applying a tourniquet or manual compression over the superficial veins and then asking the patient to stand up. This test is called the Brodie .
Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy of the great saphenous vein using foam sclerosants is best performed with the leg elevated and no occlusive pressure at the saphenofemoral junction in order to reduce the risk of gas embolization to the central nervous system. Further study is needed to assess the mid . The optimal treatment approach for patients with active venous leg ulcers (VLUs) and post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) associated with great saphenous vein (GSV) reflux remains unclear. To address this gap, we retrospectively compared the outcomes of patients with post-thrombotic VLU with an intact GSV vs those with a stripped or ablated GSV. Great saphenous vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot blocks one of your great saphenous veins. Only rarely does it travel to your lungs, possibly leading to a dangerous pulmonary embolism. The medial marginal vein helps form the origin of the great saphenous vein and drains blood from the sole of the foot.; The small saphenous vein drains the lateral surfaces in the upper foot, ankle, and parts of the leg.; Tibial veins—of which there is an anterior and a posterior one—drain from the foot, ankle, and leg, before uniting and forming the popliteal vein .
We recommend that a complete duplex ultrasound scanning examination for venous reflux in the lower extremities should include diameter measurements in patients with the leg in the dependent position, from the anterior to the posterior wall, at the saphenofemoral junction, in the great saphenous vein at the proximal thigh and at the knee, in the anterior accessory .
Great saphenous vein thrombosis is a type of blood clot that blocks the great saphenous vein (GSV), also known as the long saphenous vein. This large vein delivers blood from the ankle, lower leg, and thigh to the .Next, the great saphenous vein in the upper part of the thigh is occluded with manual compression, and the patient stands. The clinician keeps the vein occluded while watching for venous filling in the leg. Which test is being performed?An APRN evaluating a pt for valvular competency in the communicating veins of the saphenous system, starts with the patient supine, then elevates on leg to about 90 deg to empty it of venous blood. Next, the great saphenous vein in the upper part of the thigh is occluded with manual compression, and the pt stands. Venous reflux may occur in all parts of the great saphenous vein (GSV). The GSV diameter generally increases when venous reflux occurs, and the extent of venous dilation may be altered on the basis of size and location of the reflux within the GSV. We examined which part of the GSV is the most sensitive and dilated in association with venous reflux.
Notes: Color-Doppler is used to identify the great saphenous vein (GSV) in its fascial sheath (long arrow). A 4.2mm perforating vein (short arrow) communicates with the GSV. Reflux is determined by compressing and rapidly releasing the distal leg (green arrow) and duration of reversal of flow is identified and measured (x) at the beginning of flow reversal. The medical uses of the saphenous vein are still being researched. Walls of the Great Saphenous Vein. The great saphenous vein’s walls can be broken down into three layers of tissue: The inner layer, called the tunica intima, is lined with smooth cells that make it easy for blood to flow through the vein itself. The Vein Book. 2nd ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 2014. 3-16. Dwerryhouse S, Davies B, Harradine K, Earnshaw JJ. Stripping the long saphenous vein reduces the rate of reoperation for recurrent varicose veins: five-year results of a randomized trial. J Vasc Surg. 1999 Apr. 29 (4):589-92. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. Recek C.Superficial vein thrombosis was classically regarded as benign. However, modern data suggests that saphenous vein thrombosis may actually co-exist at the time of diagnosis with deep vein thrombosis or even pulmonary embolism. Furthermore, saphenous vein thrombosis may also propagate or embolize to more severe forms of venous thromboembolism.
Perform the manual compression test by having the patient stand and placing your right hand over the distal lower part of the varicose vein and your left hand over the proximal vein. Your hands . The Society for Vascular Surgery (SVS) and the American Venous Forum (AVF) have developed clinical practice guidelines for the care of patients with varicose veins of the lower limbs and pelvis. The document also includes recommendations on the management of superficial and perforating vein incompetence in patients with associated, more advanced chronic .
Venous disease has a very high prevalence among adults, ranging from 40% to 80%, and the highest prevalence is in Western countries.[1] In the United States alone, greater than 30% of adults are affected by chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins. Chronic venous insufficiency can result in pain and loss of workdays and thereby result in significant .
The great saphenous vein is by far the most frequently examined and treated vein of all the superficial veins. Furthermore, the majority of venous studies are performed on the great saphenous vein. . The test leg should be dependent, . These include vein compression with the probe, manual calf compression or the Wunstorf manoeuvre. The main .
conclusion of rockwell hardness testing machine
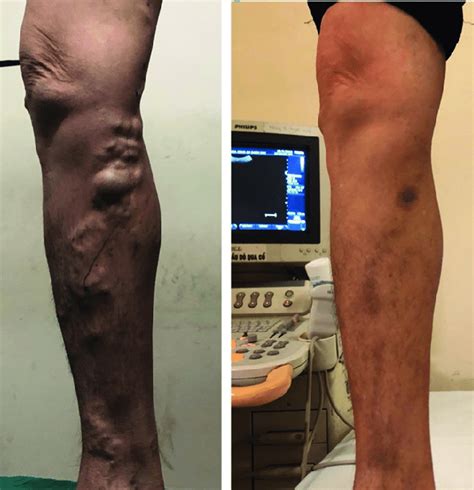
varicose veins with gsv
high saphenous vein ligation evaluation
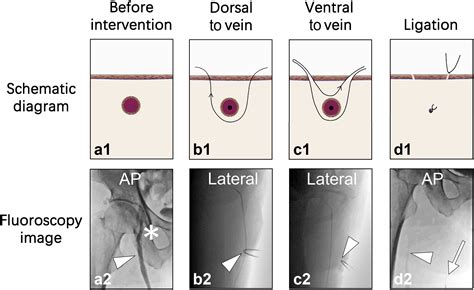
webExtremely violent Physics-based sandbox game with lots of custom content, active ragdoll physics and gore for fun, killing time, and stress relief. Most popular community and official content for the past week.
manual compression test great saphenous vein|varicose veins with gsv